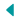
Bolivia lies in the central zone of South America, between the meridians 57º 26 ‘and 69º 38’ of longitude of the meridian of Greenwich and the parallels 9º 38 ‘and 22º 53’ of south latitude. Its 1,098,581 km² surface area extends from the Central Andes and part of the Chaco to the Amazon. The geographical center of the country is located in the area of Puerto Estrella on the Rio Grande in the province of Ñunflo de Chaves, located in the department of Santa Cruz.
The geographical location of the country provides a wide variety of land relief forms and climates. There is a wide biodiversity (considered among the largest in the world), as well as different ecological regions and subunits such as the Altiplano, the Amazon plain, the dry valleys, the Yungas and the Chiquitano mountain ranges that are framed between 70 meters above sea level (masl) (near the river Paraguay) and 6542 masl (Nevado Sajama). In spite of the variety of geographical contrasts, Bolivia lacks coastline (condition acquired after War of the Pacific in 1879).
Bolivia is divided into three physiographic regions:
Andean Region in the southwest
With 28% of the national territory (307 603 km²), this zone is located at more than 3000 msnm, located between the two great Andean branches:
The Cordilleras Occidental and Oriental, which present some of the highest peaks in America such as Nevado Sajama (6542 masl) and Illimani (6462 masl). In this region is Lake Titicaca, the highest navigable in the world located at 3810 masl, with an extension of 8,100 km² and shared with Peru. The average temperature during the day is between 15 to 20 ° C.
Here, in the South Altiplano is the Uyuni Salt Flat or Thunupa Salt Flat, an emblematic tourist destination of the country, which is not only the largest salt desert in the world with an area of 10 582 km² and a maximum depth of 120 meters, But also the largest lithium reservoir in the world and the largest flat surface.
It is located at 3.660 meters above sea level, in the department of Potosí, surrounded by mountains and volcanoes that reach 5,000 meters high.
Sub-Andean region in south-central
Between the Altiplano and the eastern plains that covers 13% of the territory (142 815 km²), includes Valleys and Yungas (2500 masl). It is characterized by its agricultural activity and its warm to warm climate (15 to 25 C). It is an ecological floor suitable for the production of coca leaf (Erythroxylum coca), medicinal plant, food and ritual use highly respected by the Andean peoples.
Region of the Llanos in the northeast
Covers 59% of the national area with an extension of 648,163 km² and is located to the north of the Eastern mountain range, that extends from the foot of the Andes towards the river Paraguay. It is a land of plains and low plateaus, covered by extensive forests rich in flora and fauna. The region is marked as being less than 400 masl. It has extensive rivers and the largest biodiversity in the country. It registers an average annual temperature of 25 to 30ºC.